SafeBreach Labs has updated the Hacker’s Playbook™ with new attack methods for a relatively new threat group Darkside whose ransomware strain dominated headlines over the weekend by attacking the Colonial Pipeline and causing disruptions to the oil distribution infrastructure in the Eastern US. This ransomware follows the double extortion trend, which means that the threat actors not only encrypt the user’s data, but first exfiltrate it and threaten to make it public if the ransom is not paid.
The Darkside group has been active since Fall of 2020 and its typical targets include critical US infrastructure entities as well as organizations in the manufacturing, legal, insurance, healthcare, and energy sectors. Their ransomware has been observed using a combination of Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP) over Tor, Cobalt Strike remote access tool, and several PowerShell tools.
Several of the attack techniques used by Darkside can be mapped to the MITRE ATT&CK® framework, including – T1059, T1053, T1140, T1036, TT1555, T1087, T1082, T1105, TT1489, and T1486. The SafeBreach platform allows organizations to operationalize the ATT&CK framework and validate their security controls against evolving attack techniques (including those used by Darkside). SafeBreach has updated the attack playbook to include two new techniques used by Darkside bringing the total number of supported Darkside attack techniques to 27.
2 newly developed playbook methods related to Darkside Ransomware
- #6369 – Communication with Darkside using HTTP (Infiltration)
- #6370 – Communication with a real malicious Darkside server using HTTP/S (Infiltration)
25 existing playbook methods related to Darkside Ransomware
- #6182 – Transfer of Darkside malware over HTTP/S
- #6184 – Email Darkside malware as a ZIP attachment
- #6183 -Transfer of Darkside malware over HTTP/S
- #6185 – Email Darkside malware as a ZIP attachment
- #6180 – Pre-execution phase of Darkside malware
- #6181 – Write Darkside malware to disk
- #2293 – Create and Start a Service
- #2248 – Masquerading
- #2222 – Discover Remote Systems using PowerShell
- #806 – Collect Files using ZIP
- #6127 – Extract LSASS memory dump using PowerShell and Rundll32
- #5307 – Event Triggered Execution using PowerShell Profile
- #5107 – Stop a service using net stop command
- #3820 – Extract credentials stored in a browser using WebBrowserPassView
- #312 – Obfuscation of EXE inside Encrypted ZIP over HTTP protocol
- #2611 – Extract system date using PowerShell
- #214 – Scheduled task creation over SMB
- #1693 – Collect Windows system data using CMD
- #1269 – Creating Windows schedule task (schtasks)
- #110 – Covert data asset exfiltration using HTTP/s POST
- #109 – Covert data asset exfiltration using HTTP/s GET
- #106 – Covert data exfiltration using HTTP (GET)
- #105 – Covert data asset exfiltration using HTTP (URI)
- #2174 – Extract users and groups using net.exe (Windows)
- #2164 – Scheduled Task
What you should do now
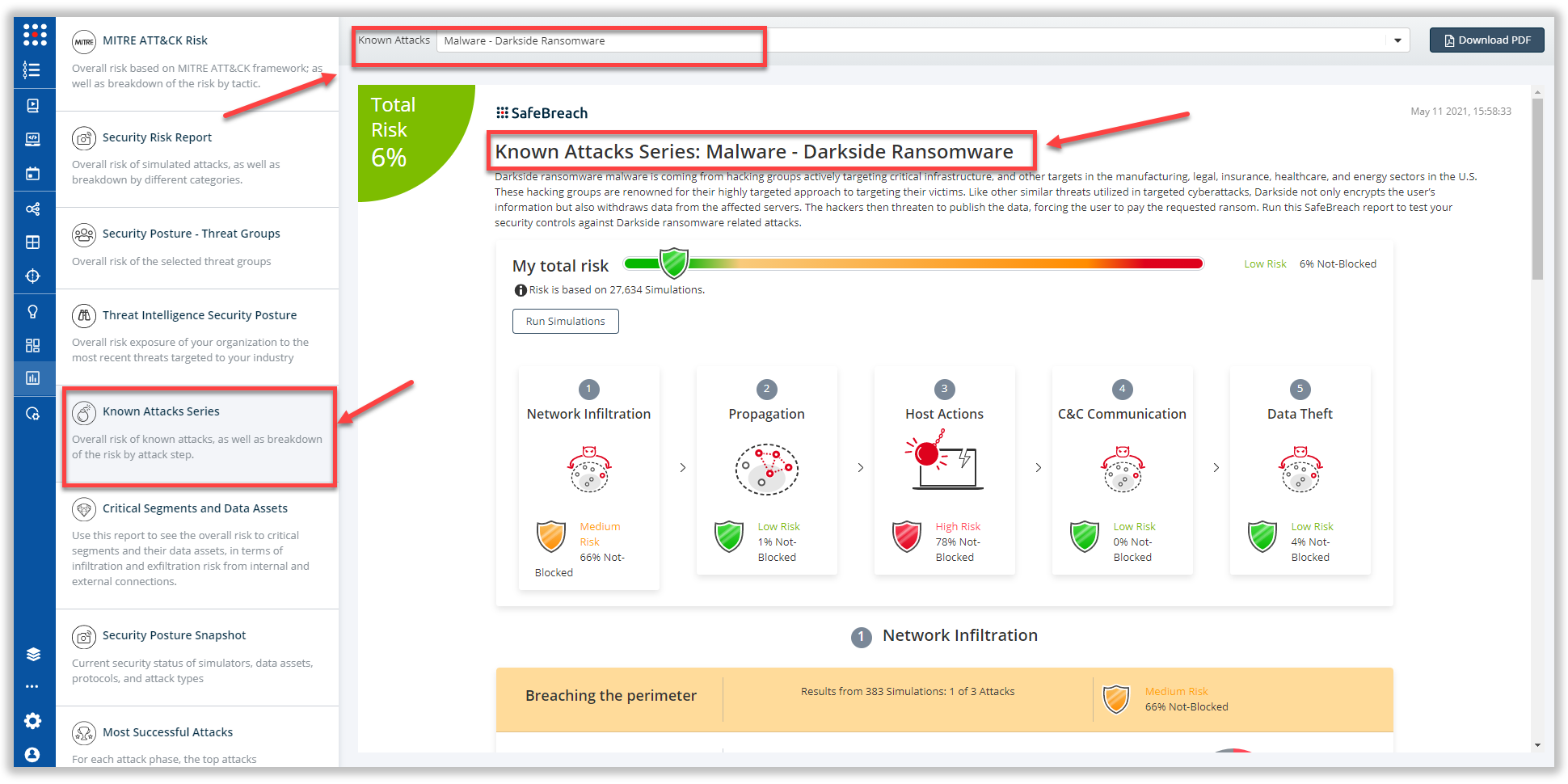
The new attack methods utilized by the Darkside ransomware are already in the SafeBreach Hacker’s playbook and ready to be run across your simulators. The Known Attack Series report has been updated so you can run the specific attacks from this specific threat group. From the Known Attack Series report, select “Malware: Darkside Ransomware” report and select “Run Simulations” which will run all attack methods.