On April 18th, Federal Bureau of Investigation (FBI), the Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA), and the U.S. Treasury Department (Treasury) issued a joint advisory highlighting the cyber threat associated with a North Korean APT group involved in cryptocurrency thefts since 2020. Additional details about this threat and the associated tactics, techniques, and procedures (TTPs) are available in US-CERT Alert (AA22-108A) TraderTraitor: North Korean State-Sponsored APT Targets Blockchain Companies.
Stealing Cryptocurrency to Fund the North Korean Regime
The North Korean APT group responsible for these attacks is the Lazarus group (also known as APT 38, BlueNoroff, and Stardust Chollima). As of April 2022, the U.S. government observed this APT group targeting a variety of organizations in the blockchain technology and cryptocurrency industry, including cryptocurrency exchanges, decentralized finance (DeFi) protocols, play-to-earn cryptocurrency video games, cryptocurrency trading companies, venture capital funds investing in cryptocurrency, and individual holders of substantial amounts of cryptocurrency or valuable non-fungible tokens (NFTs).
Attacks involving malware-laced cryptocurrency applications referred to as TraderTraitor involves the social engineering of victims using a variety of communication platforms to encourage individuals to download trojanized cryptocurrency applications on Windows or macOS operating systems. The cyber actors then use the applications to gain access to the victim’s computer, propagate malware across the victim’s network environment, and steal private keys or exploit other security gaps. These activities enable additional follow-on activities that initiate fraudulent blockchain transactions.
These actors will likely continue exploiting the vulnerabilities of cryptocurrency technology firms, gaming companies, and exchanges to generate and launder funds to support the North Korean regime. Last year, the FBI, CISA, and US Department of Treasury also shared information on malicious and fake crypto-trading applications injected with AppleJeus malware used by Lazarus to steal cryptocurrency from individuals and companies worldwide.
Technical details about TraderTraitor
- The intrusions begin with a large volume of spear phishing messages sent to employees of cryptocurrency/blockchain companies working as system administrators, software developers, or as IT DevOps engineers.
- These messages mimic recruitment efforts and offer high-paying jobs to entice recipients to download malware-laced cryptocurrency applications, referred to as TraderTraitor by the U.S. government
- The malicious applications are written using cross-platform JavaScript code with the Node.js runtime environment using the Electron framework. The malicious applications are derived from a variety of open-source projects and purport to be cryptocurrency trading or price prediction tools.
- The TraderTraitor applications are pushed via websites featuring modern design advertising the fake crypto apps’ alleged features.
- The advisory highlights the following malicious TraderTraitor cryptocurrency applications:
- DAFOM: a “cryptocurrency portfolio application” (macOS)
- TokenAIS: claims to help “build a portfolio of AI-based trading” for cryptocurrencies (macOS)
- CryptAIS: claims to help “build a portfolio of AI-based trading” (macOS)
- AlticGO: claims to offer live cryptocurrency prices and price predictions (Windows)
- Esilet: claims to offer live cryptocurrency prices and price predictions (macOS)
- CreAI Deck: claims to be a platform for “artificial intelligence and deep learning” (Windows and macOS)
IMPORTANT NOTE for SafeBreach Customers – Coverage for AA22-108A
As soon as details and IOCs for TraderTraitor were first available, corresponding attacks were immediately added to the SafeBreach Hacker’s Playbook™ on April 19th. Attacks pertaining to the newly discovered TraderTraitor malware are now available in the playbook and ready to run individually or as part of the AA22-108A TraderTraitor Malware scenario. We encourage you to evaluate your preparedness against TraderTraitor and Lazarus Group by running the attacks listed below. Additionally, we would also recommend you validate/revalidate your controls against attacks identified in US-CERT AA21-048A (AppleJeus).
7 newly added playbook methods for TraderTraitor:
- #7006 – Write TraderTraitor malware to disk (host level)
- #7007 – Transfer of TraderTraitor malware over HTTP/S (lateral movement)
- #7008 – Transfer of TraderTraitor malware over HTTP/S (infiltration)
- #7009 – Email TraderTraitor malware as a ZIP attachment (lateral movement)
- #7010 – Email TraderTraitor malware as a ZIP attachment (infiltration)
- #7011 – Communication with TraderTraitor using HTTP (infiltration)
- #7012 – Communication with a real malicious TraderTraitor server using HTTP (infiltration)
What you should do now
Attack methods related to US-CERT AA22-108A (TraderTraitor) are ready to run across your simulators. The Known Attack Series report has been updated so you can run the specific attacks from this US-CERT alert. From the Known Attack Series report, select the US-CERT AA22-108A (TraderTraitor) report and select Run Simulations which will run all attack methods.
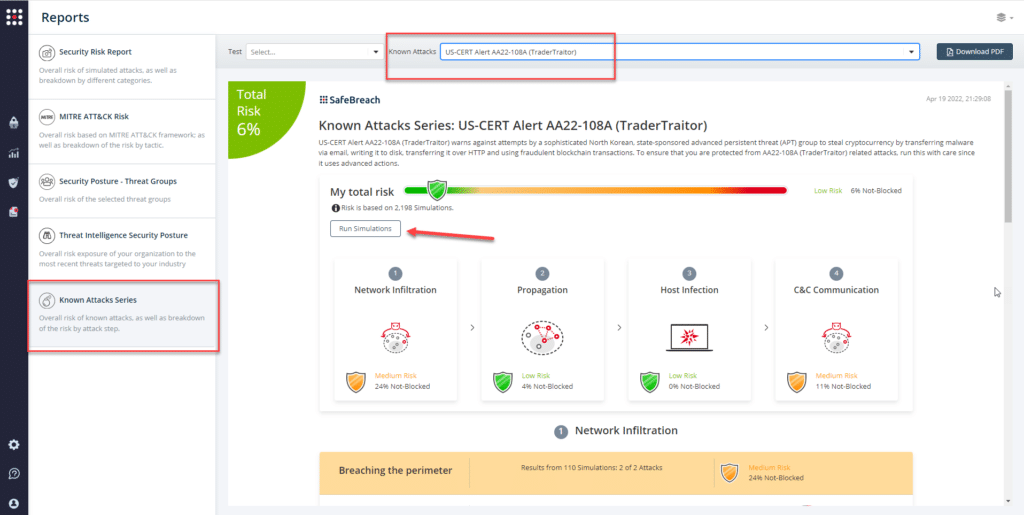
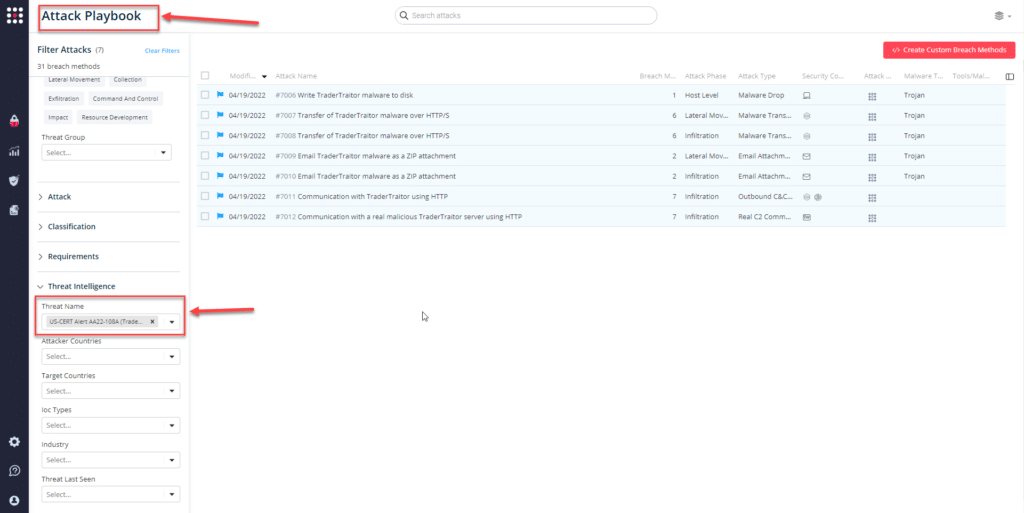
You can also select all the attacks related to US-CERT AA22-108A (TraderTraitor), by going to the SafeBreach Playbook and filtering by Threat Name – US-CERT AA22-108A (TraderTraitor)
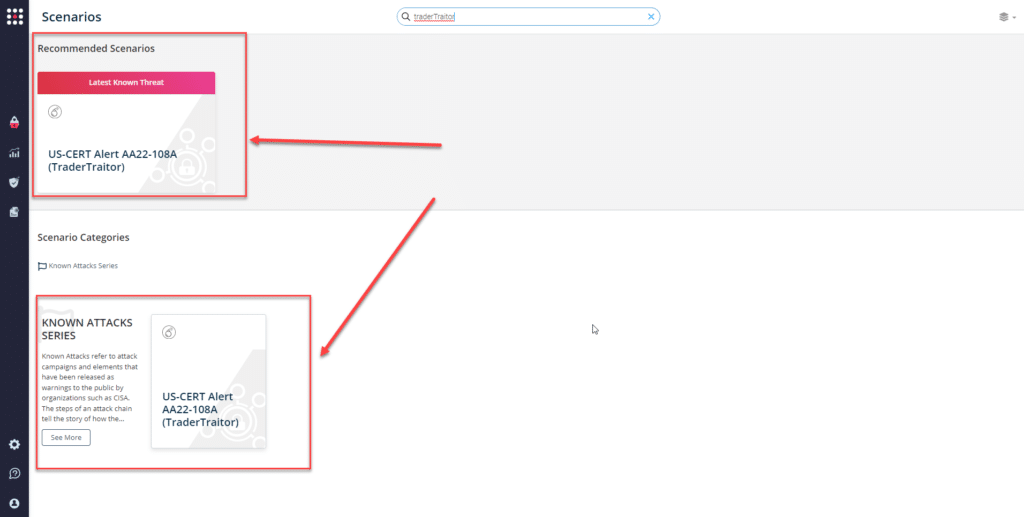
or you can go to the “SafeBreach Scenarios” page and choose the US-CERT AA22-108A (TraderTraitor) scenario from the list of available scenarios.
NOTE – The following actions have been recommended to mitigate cyber threats to cryptocurrency:
- Patch all systems.
- Prioritize patching known exploited vulnerabilities.
- Train users to recognize and report phishing attempts.
- Use multifactor authentication.
Additional Useful Resources –